Yes—most functional mushrooms like Lion’s Mane, Reishi, Chaga, and Cordyceps are legal for sale and personal use in the U.S. and many other countries. They’re generally classified as dietary supplements, but legality varies by region, claims made, and how the product is formulated.
If you’ve been eyeing that slick-looking mushroom gummy promising brain boosts or stress relief, you’re not alone, and you’re not crazy to ask: “Wait, is this legal?”
With more brands pushing the limits of natural nootropics, and with psychoactive decriminalization news making headlines, it’s easy to confuse functional mushrooms with their trippy cousins. But here’s the truth:
Functional mushrooms aren’t about hallucinations, they’re about function.
Think: mental clarity, immune support, or creative flow. No psilocybin. No party tricks. Just fruiting body extracts (ideally), backed by traditional use and emerging science.
Still, legality isn’t just black and white, it’s a colorful mess of supplement laws, marketing restrictions, and import weirdness that can get your Lion’s Mane seized by customs if you’re not careful.
This guide breaks it all down:
- Where functional mushrooms are legal
- What gets them flagged (hint: it’s usually not the mushroom)
- How to stay compliant as a buyer or brand
- And why “legal” doesn’t always mean simple
Let’s get clear, not caught.
What Are Functional Mushrooms (and What Makes Them Legal?)

Not all mushrooms make you see God, or get you arrested. Some just help you focus, breathe deeper, or bounce back from a rough night faster.
Functional mushrooms are non-psychoactive species known for their adaptogenic, immune-supporting, and cognitive-enhancing properties. They include:
- Lion’s Mane – supports memory, focus, and nerve growth
- Reishi – known for calming effects and immune balance
- Cordyceps – linked to stamina and cellular energy
- Turkey Tail – studied for gut and immune support
- Chaga – antioxidant-rich, supports inflammation response
Why They’re Legal (Unlike Psilocybin)
These mushrooms don’t contain controlled substances like psilocybin or muscimol. That means they’re not classified as drugs in the U.S., Canada, EU, or Australia.
In the U.S., they fall under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA). That gives brands permission to sell them, but not to claim they cure diseases. That’s the legal line.
What Legality Looks Like in Practice
- You can buy them over the counter or online
- No prescription needed
- No Schedule I classification
- No psychoactive compounds
- Label must include disclaimers like “not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease”
They’re regulated like protein powder or vitamin C—not like cannabis or psychedelics.
But here’s where it gets messy: Not all mushrooms are treated the same in every country, and how they’re processed (mycelium vs. fruiting body, extract vs. powder) can influence legal treatment.
Functional vs. Psychedelic Mushrooms: Clearing the Confusion
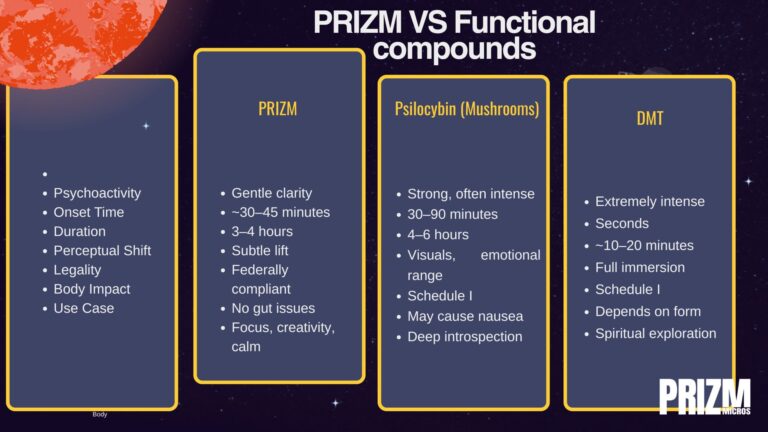
Here’s the truth: just because a mushroom supports your mood doesn’t mean it’s a psychedelic. But that line gets blurred fast, especially when your gummies say things like “elevated clarity” or “cosmic calm.”
So let’s break it down.
Functional Mushrooms (Legal, Non-Psychoactive)
These are the wellness all-stars: Lion’s Mane, Reishi, Cordyceps, Chaga, Turkey Tail. They’ve been used for centuries in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine, and they’re fully legal in most countries.
- No psilocybin
- No trippy effects
- No DEA scheduling
They’re valued for their adaptogenic and nootropic properties, meaning they help the body manage stress and may support brain function, without making you hallucinate.
Psychedelic Mushrooms (Illegal in Most Countries)
This is where the law hits hard. Mushrooms like Psilocybe cubensis contain psilocybin, a Schedule I substance in the U.S. That means:
- Federally illegal to possess, sell, or transport
- Legal only in specific contexts (e.g., Oregon’s therapy model)
- Often confused with legal mushroom supplements due to packaging or language
Also controversial: Amanita muscaria (yes, the red one with white spots). It doesn’t have psilocybin, but it is psychoactive, thanks to muscimol and ibotenic acid. It’s legal in many places, but still alters perception.
Why This Distinction Matters
If your label hints at psychedelia, or your branding leans “microdose”, you’re crossing into gray area, legally and culturally. And for consumers, the confusion runs deep.
PRIZM Pro Tip: Always check your label. Always know your ingredients. Functional doesn’t mean psychedelic, but marketing can get you flagged anyway.
Is It Legal Everywhere? A Global Snapshot of Mushroom Laws
Functional mushrooms may be legal where you live, but cross a border, and that Lion’s Mane capsule might get flagged. Here’s what legality looks like around the world:
🇺🇸 United States
- Legal Status: Functional mushrooms like Reishi and Cordyceps are legal and classified as dietary supplements under the FDA’s DSHEA.
- Key Rule: You can’t claim they treat diseases, “supports focus” is fine; “cures anxiety” is not.
- Gray Zones: Combining mushrooms with cannabinoids like Delta-8 can trigger scrutiny, even if each ingredient is technically legal.
🇪🇺 European Union
- Legal Status: Reishi and Chaga? Usually fine. But Lion’s Mane and Cordyceps? Often flagged as “novel foods.”
- Implication: If not widely consumed in the EU before 1997, they need pre-market approval.
- Labels Matter: Mislabel “mycelium” as “fruiting body” and you could be looking at a customs seizure.
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
- Post-Brexit Playbook: The UK still shadows the EU on most food laws, including functional mushrooms.
- Twist: More flexibility is coming, but Lion’s Mane still may require FSA approval to market.
🇨🇦 Canada
- Regulatory Body: Health Canada
- Legal Status: Functional mushrooms are sold under the Natural Health Products framework.
- Pro Tip: You’ll need an NPN (Natural Product Number) for each item—and evidence to back up any claims.
🇦🇺 Australia
- Tightly Controlled: Treated as either complementary medicine or functional food.
- Barriers: Expect ingredient breakdowns, safety documentation, and TGA registration.
- Customs Delay Warning: Even personal-use packages get flagged without proper labeling.
Global Travel & Import Nuances
- Can I bring mushroom gummies in my carry-on? Maybe—but it depends on:
- Country-specific laws
- Labeling clarity (no vague “mind-blend” phrasing)
- Packaging (avoid powdery zip-locks—seriously)
TL;DR: Functional doesn’t mean frictionless. Legality varies by country, and enforcement often comes down to packaging, claims, and customs interpretation.
How Functional Mushrooms Are Regulated (and Why Claims Matter)
Just because functional mushrooms are legal doesn’t mean it’s a free-for-all. In fact, what you say about them matters just as much as what’s inside. Here’s how the world’s regulators keep the mushroom market in check, and why your label might be your biggest liability.
U.S. Framework: Structure Over Hype
In the U.S., functional mushrooms like Reishi, Chaga, and Lion’s Mane fall under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA):
- Allowed: Structure/function claims like “supports immune health” or “helps focus.”
- Banned: Disease claims like “treats depression” or “cures Alzheimer’s.”
- Must-Have: The disclaimer, “This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.”
- Enforcement: Rare, but real. The FDA has issued warning letters for misleading claims, especially those linking mushrooms to serious health conditions.
EU Rules: Prove It or Lose It
Under the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA):
- Claims: Must be pre-approved and backed by scientific evidence.
- Novel Foods: Ingredients like Lion’s Mane may require pre-market authorization unless consumed widely before 1997.
- Reality Check: If it’s not in the EU Novel Foods Database, you’re not selling it without a legal review.
Canada: Natural, But Regulated
Health Canada treats functional mushrooms as Natural Health Products (NHPs):
- Products need an NPN (Natural Product Number).
- Claims must be supported by peer-reviewed studies or traditional-use monographs.
- Importers must show documentation, personal packages get seized without proper labeling.
Australia: No Room for Fluff
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) demands rigor:
- Functional mushrooms are either complementary medicine or functional food, depending on format and claims.
- Brands must submit evidence of safety and efficacy.
- Noncompliant language or weak documentation? Expect bans or product holds.
What Makes a Claim Illegal (Everywhere)
“Cures anxiety”
“Reverses memory loss”
“Better than antidepressants”
“Produces a legal high”
“Supports memory”
“Promotes relaxation”
“Contains 500mg dual-extracted Lion’s Mane (30% beta-glucans)”
Bottom Line: Stick to the facts. If your product makes people feel good—great. But if your label reads like a prescription ad, you’re inviting trouble.
Functional vs. Psychedelic Mushrooms – Where the Legal Line Is Drawn
Let’s cut through the fog: not all mushrooms are trippy, and not all mushroom products flirt with legality. But a surprising number of people still lump Lion’s Mane in with psilocybin. Here’s how to tell them apart, and why it matters more than ever.
What Are Functional Mushrooms?
Think of them as your daily dose of clarity, minus the side effects. These include:
- Lion’s Mane (focus, neuroplasticity)
- Reishi (stress resilience)
- Cordyceps (energy)
- Chaga (antioxidants)
- Turkey Tail (immune support)
Key Traits:
- 100% legal in most countries
- Non-psychoactive
- Commonly sold as supplements, powders, or gummies
- No psilocybin, muscimol, or controlled substances
They’re classified as dietary supplements, natural health products, or functional foods, depending on where you live.
What Are Psychedelic Mushrooms?
This is where things get risky (and often illegal):
- Psilocybe cubensis (psilocybin content)
- Amanita muscaria (muscimol and ibotenic acid)
Key Risks:
- Psilocybin is Schedule I in the U.S. and banned in most countries.
- Amanita is legal in some U.S. states but still psychoactive and not FDA-approved.
- Products that hint at “microdosing,” “trip,” or “legal high” are often flagged, even if they don’t contain scheduled substances.
Why the Distinction Matters
Mixing up the two—even in branding—can land you in hot water:
- Customs Seizures: Legal mushrooms have been seized due to vague labels or “trippy” language.
- E-commerce Bans: Platforms like Amazon and Shopify crack down on “psychedelic-adjacent” marketing.
- Consumer Confusion: People report drug-test fears or health questions to providers based on unclear product types.
Bottom Line:
If your mushroom doesn’t contain controlled substances, it’s functional, not psychedelic. But the way you label and describe it can still get you banned, banned, or sued.
Clarity isn’t just good branding. It’s legal protection.
Can Functional Mushrooms Cause Legal Trouble Anyway?
You’ve done your research. You know Lion’s Mane isn’t psilocybin. But somehow your supplement still got seized, or your HR rep asked weird questions after your wellness check. What gives?
Here’s where functional mushrooms—despite being legal—can still trip you up (pun intended).
Customs Confusion: Why Legal ≠ Risk-Free at Borders
Even if your product is totally above board, international travel gets sticky:
- Vague Labeling: Packages without clear ingredients get flagged.
- Foreign Language Packaging: Customs agents may seize items they can’t verify.
- Product Format: Powders and capsules can be mistaken for illicit substances.
Pro tip: Always bring products in original packaging with ingredient lists and avoid using euphemisms like “herbal trip blend” on customs forms.
Drug Testing Worries: Can Functional Mushrooms Cause False Positives?
Short answer: No, functional mushrooms like Lion’s Mane or Reishi do not show up on standard drug tests. They don’t contain psilocybin, THC, or other flagged compounds.
That said, confusion happens:
- Uninformed Testers: Some employers or providers may flag mushroom use out of ignorance.
- Stacked Supplements: Products mixed with hemp derivatives (like Delta-8) can cause positives.
Solution: Know your ingredients and ask brands for a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) before you dose.
Red Flags That Can Get You Banned from Marketplaces
Whether you’re a buyer or a seller, language matters:
- “Microdose” = 🚩
- “Trippy calm” = 🚩
- “Psychedelic vibe” = 🚩
Even if the product is legal, using those terms can get listings pulled from Amazon, Etsy, or Shopify.
Best practice: Stick to structure-function claims like “supports memory” or “promotes focus”—not “mimics LSD but legally.”
Summary: Stay Smart, Stay Legal
Functional mushrooms are legal. But platforms, customs, and employers may not know the difference. So:
- Use precise, transparent labeling.
- Avoid words that sound like psychedelics.
- Ask for third-party lab tests to back it all up.
Functional Mushroom Legality Around the World: Know Before You Dose
Functional mushrooms might be having a global glow-up—but their legal status still depends on where you live (or ship to). Here’s what’s legal, what’s risky, and how to stay on the right side of the law, country by country.
🇺🇸 United States
- Legal under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA).
- No pre-approval needed if you follow Good Manufacturing Practices and don’t claim to treat disease.
- Structure/function claims: “Supports focus,” “Promotes immune health.”
- Illegal: “Cures depression,” “Treats anxiety.”
- Watch out for state-level variation, especially if your product includes cannabinoids or exotic enhancers.
🇨🇦 Canada
- Functional mushrooms are legal as Natural Health Products (NHPs).
- Must apply for a Natural Product Number (NPN) with supporting evidence.
- Imports without NPNs can be seized at the border.
- Self-import loophole exists: individuals face fewer restrictions than businesses.
🇪🇺 European Union
- Depends on the mushroom:
- Reishi, Chaga = Generally accepted.
- Lion’s Mane, Cordyceps = Often flagged as “novel foods.”
- Reishi, Chaga = Generally accepted.
- EFSA approval needed for anything not consumed in the EU before 1997.
- Health claims must be pre-authorized and evidence-backed.
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
- Similar to the EU, but carving its own path post-Brexit.
- FSA regulates mushrooms as food or supplement.
- Lion’s Mane likely needs novel food approval.
- Products must avoid unapproved health claims.
🇦🇺 Australia
- Mushrooms are treated as complementary medicines or functional foods.
- Governed by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
- Requires documentation of safety and efficacy.
- Customs delays are common, labeling and clarity are essential.
Traveling with Functional Mushrooms?
- Pack in original packaging.
- Declare when necessary, especially if traveling to Australia or the EU.
- Avoid vague labels like “neuro blend” or “adaptogenic stack.”
Key Takeaways for Global Buyers & Sellers
- Always check local laws before importing or selling.
- Get familiar with GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe), NHP, and Novel Food classifications.
- Third-party testing and transparent labeling help avoid customs issues and build trust across borders.
How to Shop Smart: Avoid the Sketchy Stuff, Trust What’s Transparent

In a market booming with buzzwords and bold claims, not every gummy is built for good vibes, or legal shelves. Whether you’re buying for focus, clarity, or just curiosity, here’s how to tell the legit stacks from the questionable ones.
The 8-Point Smart Buyer Checklist
- CoAs or It Didn’t Happen
Always look for a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a third-party lab—batch-specific, easy to scan, and ideally accessible via QR code. - Exact Ingredient Breakdown
“1,000mg mushroom blend” means nothing. Look for:
“500mg Lion’s Mane (fruiting body, 30% beta-glucans), 250mg Cordyceps, 250mg Reishi” - Clear Enhancement Stack
Psychoactives like Delta-8 or muscimol? Doses should be listed clearly. Transparency is your friend—and your safety net. - Fruiting Body Over Mycelium
Fruiting body = full-spectrum potency.
Mycelium = often filler. Bonus if it’s dual-extracted. - Platform & Seller Credibility
Reputable brands list their products on their own sites and major retailers—with regulatory info, not just vibes. - State-by-State Awareness
Legal in one state doesn’t mean legal everywhere. If the gummy contains psychoactive elements, check your local laws. - Pricing that Makes Sense
“10 gummies for $10” claiming high potency? 🚩 Quality mushroom extracts and lab testing aren’t that cheap. - Where It’s Sold Matters
If the product is only available on vape shop counters or sketchy third-party sites, think twice. No transparency = no trust.
Red Flags That Should Stop You Cold
- No lab results or CoA available
- Euphemistic blends: “Mind Matrix,” “Trippy Calm,” “Quantum Zen”
- No dosage info on psychoactive enhancers
- Suspiciously low price point for “high potency”
- Sold alongside THC products without clear distinction
Final Thoughts: Clarity Before the Dose
In the world of functional mushrooms, the question isn’t just are they legal?—it’s are they clear, safe, and what you actually think they are?
Because legality doesn’t mean much if the label’s vague, the sourcing’s shady, or the product leaves you guessing. And “enhanced” shouldn’t mean a legal gray area you didn’t sign up for.
At PRIZM Micros, we believe the journey to better mood, focus, or flow should never come at the cost of transparency. That’s why we formulate every product with clean, compliant ingredients, declare what’s inside (down to the microgram), and back it all with lab reports you can actually read—without needing a PhD in biochem or a lawyer on speed dial.
So whether you’re here for clarity, creativity, or just a feel-good lift that fits your life—you’ve got options. And the good ones? They’re built for vibes, backed by science, and totally legal.
Snackable psychedelics. PRIZM makes it possible—legally.
Disclaimer: This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Statements regarding this product have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medications, or have a medical condition. Product use is intended for adults 18+. Keep out of reach of children. Check your local laws and regulations before purchase or use. PRIZM Micros does not make any psychoactive or therapeutic claims. For legal, clearly labeled wellness only.